Los investigadores de ESET descubren un grupo APT alineado con China, —que rastreamos como PlushDaemon—, y una de sus operaciones de ciberespionaje: el compromiso de la cadena de suministro del software VPN desarrollado por una empresa surcoreana en el que los atacantes reemplazaron el instalador legítimo por uno que desplegó el implante de firma del grupo, SlowStepper: un backdoor rico en funciones con un toolkit de más de 30 componentes.
Puntos clave de este blogpost
- PlushDaemon es un grupo de amenazas alineado con China que se dedica a operaciones de ciberespionaje.
- El principal vector de acceso inicial de PlushDaemon es el secuestro de actualizaciones legítimas de aplicaciones chinas, pero también hemos descubierto un ataque a la cadena de suministro contra un desarrollador surcoreano de VPN.
- Creemos que PlushDaemon es el usuario exclusivo de varios implantes, entre ellos SlowStepper para Windows.
- SlowStepper cuenta con un amplio conjunto de herramientas compuesto por unos 30 módulos, programados en C++, Python y Go.
Resumen
En mayo de 2024, observamos detecciones de código malicioso en un instalador NSIS para Windows que los usuarios de Corea del Sur habían descargado del sitio web del software VPN legítimo IPany (https://ipany.kr/; véase la figura 1), desarrollado por una empresa surcoreana. Tras un análisis más detallado, descubrimos que el instalador desplegaba tanto el software legítimo como el backdoor al que hemos denominado SlowStepper. Nos pusimos en contacto con el desarrollador del software VPN para informarle del problema, y el instalador malicioso fue eliminado de su sitio web.
Atribuimos esta operación a PlushDaemon, un actor de amenazas alineado con China activo desde al menos 2019, involucrado en operaciones de espionaje contra individuos y entidades en China, Taiwán, Hong Kong, Corea del Sur, Estados Unidos y Nueva Zelanda.
PlushDaemon utiliza un backdoor personalizado que rastreamos como SlowStepper, y su principal técnica de acceso inicial es secuestrar actualizaciones legítimas redirigiendo el tráfico a servidores controlados por el atacante. Además, hemos observado que el grupo obtiene acceso a través de vulnerabilidades en servidores web legítimos.
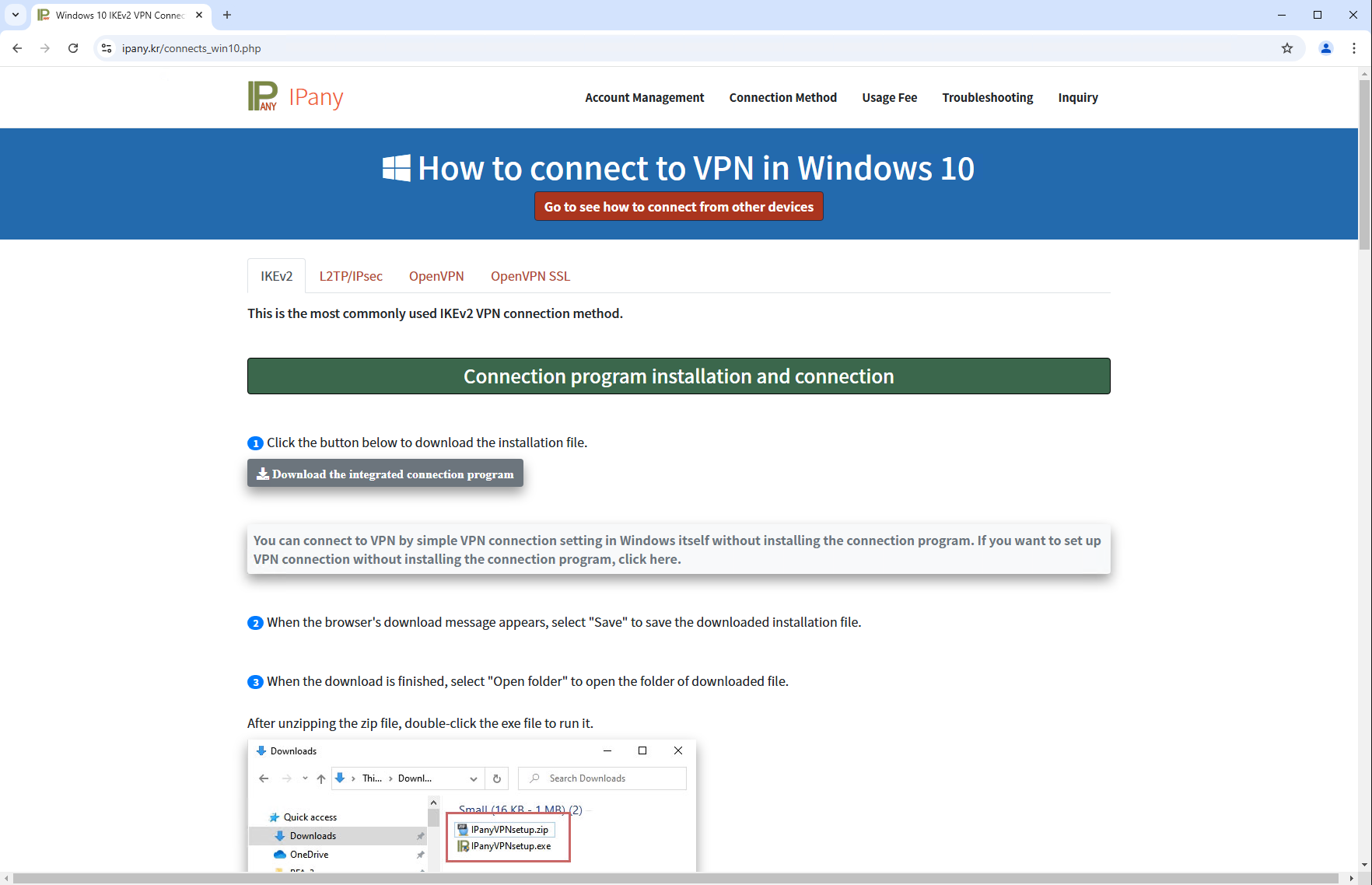
Las víctimas parecen haber descargado manualmente un archivo ZIP que contiene un instalador NSIS malicioso desde la URL https://ipany[.]kr/download/IPanyVPNsetup.zip. No encontramos ningún código sospechoso en la página de descarga (mostrada en la Figura 1) para producir descargas dirigidas, por ejemplo, mediante geofencing a regiones o rangos de IP específicos; por lo tanto, creemos que cualquiera que utilice IPany VPN podría haber sido un objetivo válido.
A través de la telemetría de ESET, descubrimos que varios usuarios intentaron instalar el software troyanizado en la red de una empresa de semiconductores y una empresa de desarrollo de software no identificada de Corea del Sur. Los dos casos más antiguos registrados en nuestra telemetría fueron una víctima de Japón en noviembre de 2023, y una víctima de China en diciembre de 2023.
Análisis técnico
Como se ilustra en la Figura 2, cuando se ejecuta el instalador malicioso IPanyVPNsetup.exe, éste crea varios directorios y despliega tanto archivos legítimos como maliciosos.
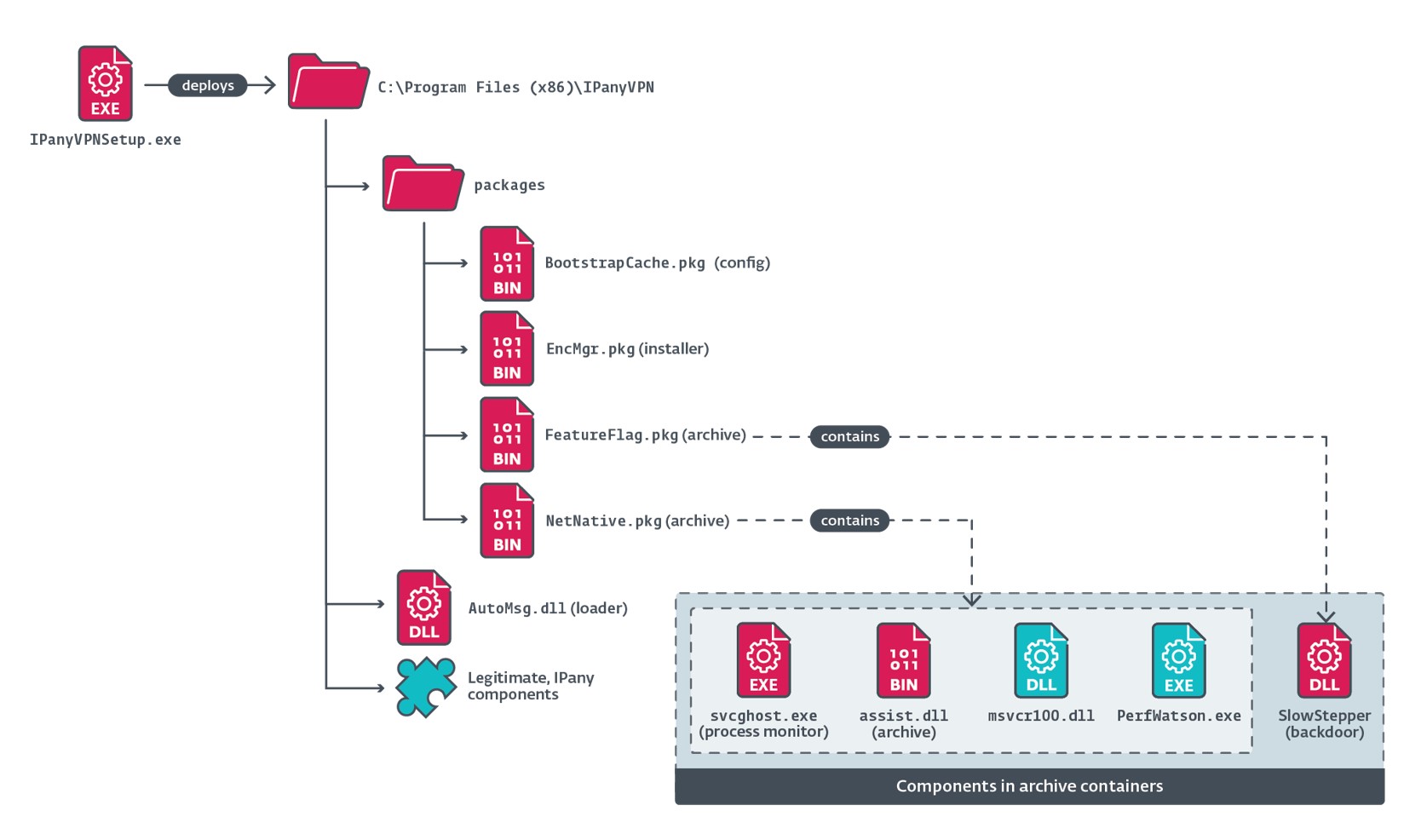
Además, el instalador establece la persistencia de SlowStepper añadiendo una entrada llamada IPanyVPN a una clave de ejecución, con el valor %PUBLIC%\Documents\WPSDocuments\WPSManager\svcghost.exe, de modo que el componente malicioso svcghost.exe (posteriormente extraído y desplegado por el cargador en EncMgr.pkg) se inicie al arrancar el sistema operativo.
El primer componente malicioso que carga el instalador es el cargador AutoMsg.dll. La Figura 3 ilustra los principales pasos que se siguen durante la ejecución de este componente.
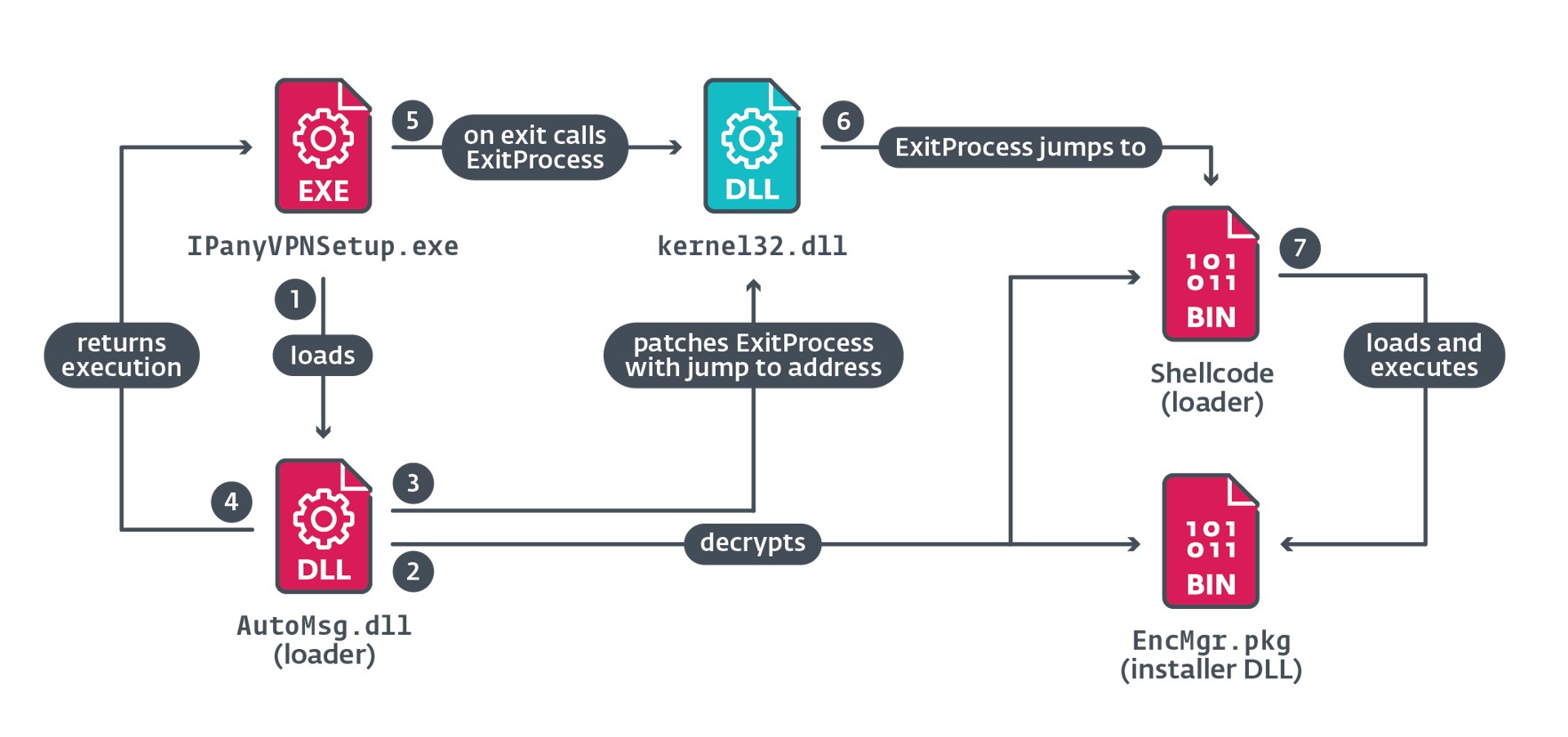
Cuando IPanyVPNSetup. exe llama a ExitProcess, los bytes parcheados redirigen la ejecución al shellcode que carga EncMgr.pkg en memoria y lo ejecuta.
EncMgr.pkg crea dos directorios - WPSDocuments y WPSManager - en %PUBLIC%\Documents y el despliegue comienza extrayendo componentes de los archivos personalizados NetNative.pkg y FeatureFlag.pkg. Los componentes se descargan en el disco y se mueven a otras ubicaciones con nuevos nombres de archivo. La secuencia y las acciones realizadas son las siguientes:
1. Extrae los archivos de NetNative. pkg a:
a. %PUBLIC%\Documents\WPSDocuments\WPSManager\assist.dll,
b. %PUBLIC%\Documents\WPSDocuments\WPSManager\msvcr100.dll,
c. %PUBLIC%\Documents\WPSDocuments\WPSManager\PerfWatson.exe, y
d. %PUBLIC%\Documents\WPSDocuments\WPSManager\svcghost.exe.
2. Elimina NetNative.pkg.
3. Mueve FeatureFlag.p kg a C:\ProgramData\Microsoft Shared\Filters\SystemInfo\winlogin.gif.
4. Mueve assist.dll a C:\ProgramData\Microsoft Shared\Filters\SystemInfo\Winse.gif.
5. Extrae el archivo de Winse. gif a %PUBLIC%\Documents\WPSDocuments\WPSManager\lregdll.dll.
6. Copia los datos de BootstrapCache.pkg a %PUBLIC%\Documents\WPSDocuments\WPSManager\Qmea.dat.
Sus últimas acciones son ejecutar svcghost.exe utilizando la API ShellExecute y luego salir.
El componente svcghost.exe realiza la monitorización del proceso PerfWatson.exe, donde se carga el backdoor, asegurándose de que siempre está en ejecución. Si los procesos no se están ejecutando, ejecuta PerfWatson.exe (originalmente una utilidad de línea de comandos legítima llamada regcap.exe, incluida en Visual Studio), de la que los atacantes abusan para cargar lateralmente lregdll.dll. El objetivo de la DLL es cargar el backdoor SlowStepper desde el archivo winlogin.gif.
En un nuevo hilo, crea una ventana sin nombre que ignora todos los mensajes excepto WM_CLOSE, WM_QUERYENDSESSION y WM_ENDSESSION. Cuando se recibe cualquiera de estos tres mensajes, el hilo intenta establecer persistencia en el registro de Windows, dependiendo de los permisos del proceso actual; ver Tabla 1.
Tabla 1. Claves del registro objetivo para la persistencia
| Requires | Registry key | Entry | Value |
| Administrator | HKLM\Software\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon | Userinit | Current path of svcghost.exe. |
| User | HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Windows | load |
El backdoor SlowStepper
SlowStepper es un backdoor desarrollado en C++ con un amplio uso de programación orientada a objetos en el código de comunicaciones del C&C. Aunque el código contiene cientos de funciones, la variante concreta utilizada en el ataque a la cadena de suministro del software IPany VPN parece ser la versión 0.2.10 Lite, según el código del backdoor. La denominada versión "Lite" contiene, en efecto, menos funciones que otras versiones anteriores y más recientes.
La versión más antigua del backdoor SlowStepper que conocemos es la 0.1.7, compilada el 2019-01-31 según sus marcas de tiempo PE; la más reciente es la 0.2.12, compilada el 2024-06-13, y es la versión completa del backdoor.
Tanto la versión completa como la Lite hacen uso de una serie de herramientas programadas en Python y Go, que incluyen capacidades para la recopilación exhaustiva de datos y el espionaje mediante la grabación de audio y vídeo. Las herramientas se almacenaban en un repositorio de código remoto alojado en la plataforma china GitCode, bajo la cuenta LetMeGo22; en el momento de escribir este artículo, el perfil era privado (Figura 4).
Comunicaciones C&C
SlowStepper no lleva la dirección IP del C&C en su configuración; en su lugar, realiza una consulta DNS para obtener un registro TXT para el dominio 7051.gsm.360safe[.]company. La consulta se envía a uno de los tres servidores DNS públicos legítimos:
- 8.8.8.8 - DNS público de Google,
- 114.114.114.114 - 114dns.com, o
- 223.5.5.5 - DNS público de Alibaba.
Obtuvimos cuatro registros de este tipo asociados a ese dominio:
- &%QT%#/zZDmb4ATTVIxwHXPLGrj0FAOV7q+P/sMG109ooj5YLnVZBs3R/eZcuQximtgLkf
- &%QT%#/zZDmb4ATTVIxwHXPLGrj0FAOV7q+P/sMG109ooj5YKQs3XiHSjM3f+h9ok9XfQ1AjoX+C4UXZsDLVqCDhvxyw==
- &%QT%#aT1sAjOFTcwzQ7hwc0iyfygP/ooo8pkIRyaNKWcqBz+QRGYBV/2v8HrVg28+aZXhfXvgDxS1vXAuhdcN2dEKxw==
- &%QT%#aT1sAjOFTcwzQ7hwc0iyfySJBEDM0z6na7BiogG0hDJqdKlUqkrb9ppOjg8epeQ6I6cUXWLKyZGZCkJwFyKD4Q==
El formato de los datos de la consulta se muestra en la Figura 5. El código comprueba si los seis primeros bytes del registro TXT coinciden con &%QT%# y, en caso afirmativo, extrae el resto de la cadena, que es un blob cifrado con AES y codificado en base64 que contiene una matriz de 10 direcciones IP que se utilizarán como servidores de C&C. La clave utilizada para el descifrado es sQi9&*2Uhy3Fg7se y el IV es Qhsy&7y@bsG9st#g.
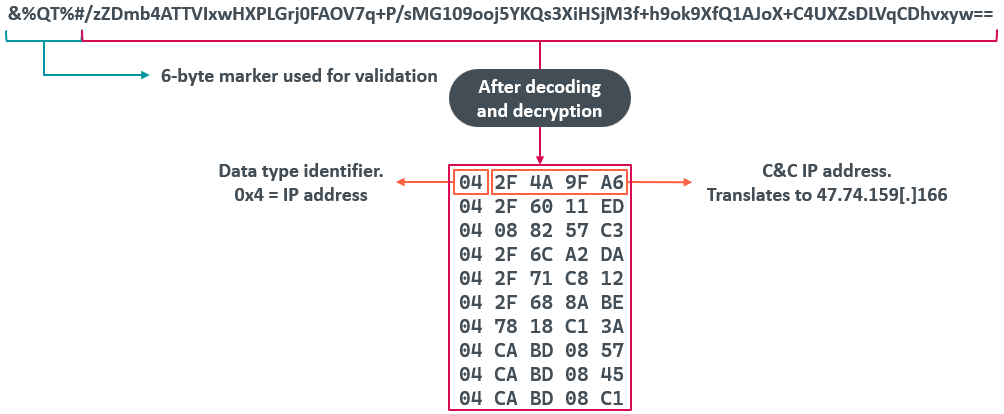
Al analizar los datos descifrados, el código puede extraer al menos cuatro identificadores de datos, descritos en la Tabla 2.
Tabla 2. Tipos de datos procesados por el backdoor Tipos de datos procesados por el código del backdoor
| Data identifier | Size of data | Description |
| 0x04 | 4 | Data is an IP address. |
| 0x05 | 6 | Data is an IP address and port number. |
| 0x06 | 16 | Skips the next 16 bytes of data. We suspect that, given the size of the data, it’s possible that it is an IPv6 address. |
| 0x00–0x03 0x07–0xFF |
Data identifier value is the value of the data size. | Skips the next (unknown) bytes of data. |
Se elige una de las direcciones IP y SlowStepper se conecta al servidor C&C vía TCP para iniciar su protocolo de comunicación. Si, tras varios intentos, no consigue establecer una conexión con el servidor, utiliza la API gethostbyname en el dominio st.360safe[.]company para obtener la dirección IP asignada a ese dominio y utiliza la IP obtenida como su servidor de C&C de reserva.
Una vez establecida la comunicación, SlowStepper puede procesar los comandos listados en la Tabla 3.
Tabla 3. Comandos básicos soportados por SlowStepper Comandos básicos soportados por SlowStepper
| Command ID | Action performed |
| 0x32 | Collects the following information from the compromised machine and sends it to the server: · brand of the CPU, using the CPUID instruction, · HDDs connected to the computer and their serial numbers, · computer name, · local host name, · public IP address, by querying multiple services, · list of running processes, · list of installed applications, · network interface information, · additional information about the computer’s drives, such as volume name and free space, · system memory, · current username, · persistence type used, · whether cameras are connected, · whether microphones are connected, · whether the operating system is running as a virtual machine, · system uptime, · HTTP proxy configuration, and · whether queries to the DNS server at 114.114.114.114:53 to resolve the addresses of two legitimate domains, cf.duba.net (Kingston) and f.360.cn (360 Qihoo), failed or succeeded. It is unclear to us what the purpose of this information is. |
| 0x38 | Executes a Python module from its toolkit; the output and any files created by the module are sent to the server. The procedure is very similar to what is used in the shell mode. |
| 0x39 | Deletes the specified file. |
| 0x3A | This command can process other commands sent by the operator in SlowStepper’s shell mode, which we explain in more detail below. Alternatively, it can also: · Run a command via cmd.exe and send the output back to the server. · Run a command via cmd.exe without sending the output to the server. |
| 0x3C | Uninstalls SlowStepper by removing its persistence mechanism and removing its files. |
| 0x3F | Lists files in the specified directory, and lists drives. |
| 0x5A | Downloads and executes the specified file. |
SlowStepper tiene una característica bastante inusual: los desarrolladores implementaron un shell personalizado, o interfaz de línea de comandos, sobre su protocolo de comunicación. Mientras que el backdoor acepta y maneja comandos de la forma tradicional, el comando 0x3A activa la interpretación de comandos escritos por el operador (Tabla 4).
Tabla 4. Comandos admitidos en modo shell Comandos admitidos en modo shell
| Command | Parameters | Description |
| cd | Path to a directory. | Checks whether a directory exists. |
| gcall | Module name and other unknown parameter(s). | This function can perform two tasks: · Download a module from the remote code repository and execute it. The module is supposed to be a console application. · Send a file from the compromised machine to the operator. |
| pycall | Tool name to be executed. | This command is explained in detail in the Execution of tools via SlowStepper’s pycall shell command section. |
| restart | self | Restarts SlowStepper by rerunning the host process and calling the ExitProcess API. Returns the message The mode of NSP doesn't support restart self. when SlowStepper is running in a process via a persistence technique that abuses Winsock namespace providers; however, it is not included in this variant of SlowStepper. |
| update | N/A | Downloads a module from the remote code repository, replacing a previous existing version. |
| gconfig | show | Displays the value of ServerIP (the C&C IP address). |
| set | Changes the value of ServerIP. The console suggests the following to the operator: If you want make the Configuration effective immediately, please command “gconfig reload”. |
|
| reload | Reloads the configuration. | |
| getname | Returns the name of the current process in which SlowStepper is running. | |
| getdll | Returns the name of the SlowStepper DLL in the current process. | |
| getpid | Returns the process ID of the current process in which SlowStepper is running. | |
| getsid | Returns the Remote Desktop Services session ID of the current process. This suggests that SlowStepper might also be intended to compromise machines running Windows Server. | |
| getpwd | Downloads getcode.mod from the remote code repository and executes it using rundll32.exe. The module generates a file, named psf.bin, that contains the collected data. | |
| gcmd | query | Creates a complete report of information about the specified file or directory. |
| delete | Deletes the specified file, directory, or all files in a directory. | |
| set | Sets configuration parameters. | |
| terminate | Terminates the specified process. | |
| cancel | Creates a file with the .delete extension. |
Ejecución de herramientas mediante el comando shell pycall de SlowStepper
La figura 6 ilustra la cadena de ejecución, comenzando cuando el operador emite un comando pycall para solicitar la ejecución de un módulo Python en la máquina comprometida; aquí, como ejemplo, el módulo CollectInfo.
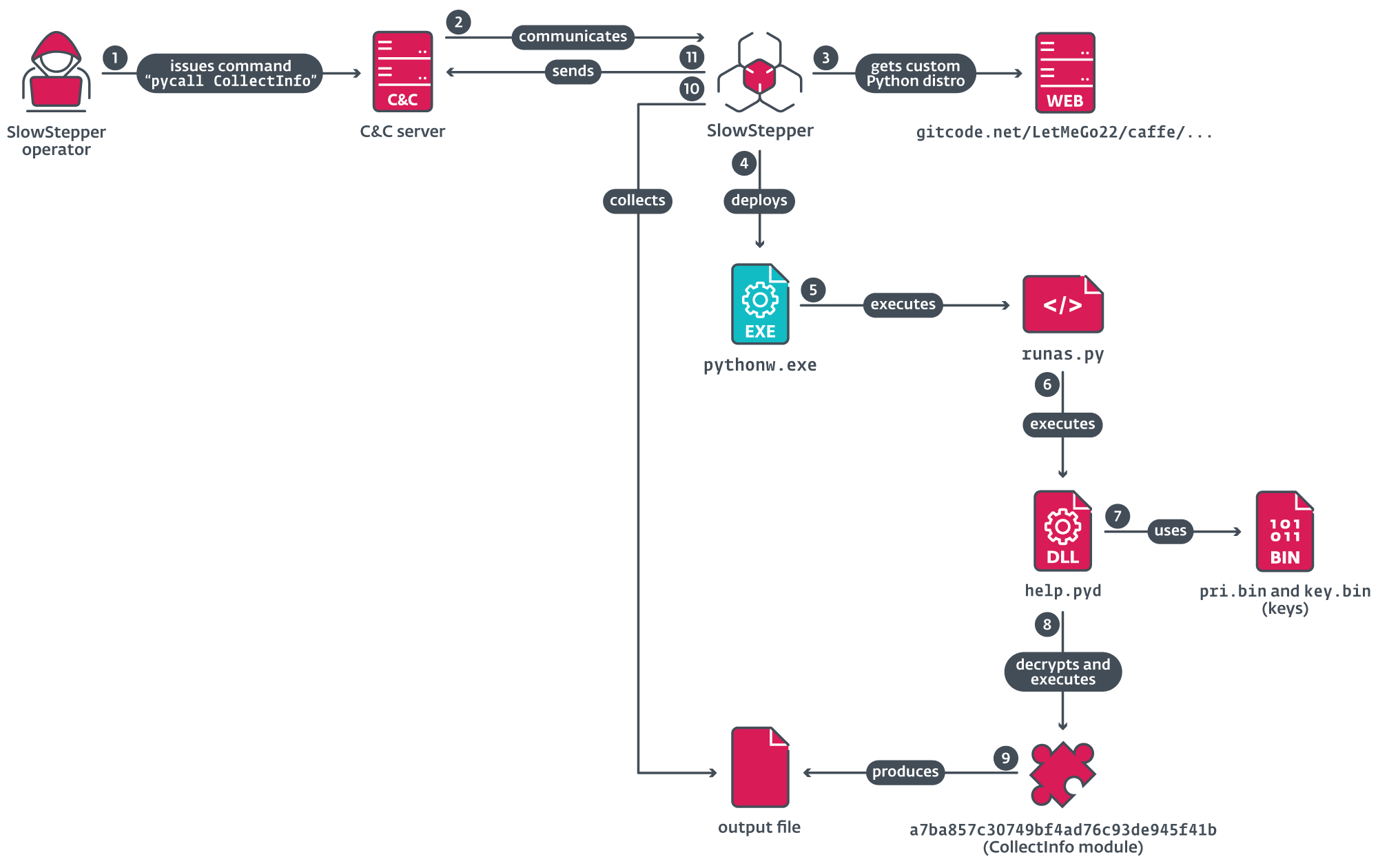
Desde el repositorio remoto, el comando pycall descarga un archivo ZIP que contiene el intérprete de Python y sus librerías de soporte. Se descarga una de las tres posibles distribuciones personalizadas, como se indica en la Tabla 5.
Tabla 5. Lista de distribuciones personalizadas de Python Lista de distribuciones personalizadas de Python y las condiciones bajo las que se descargan
| Condition | Archive name | Description |
| Windows operating system is XP. | winxppy.org | Python 3.4 |
| All required Windows API set (stub) DLLs and the Microsoft C runtime are present. | winpy_no_rundll.org | Python 3.7 |
| Neither of the preceding conditions are met. | win7py.org | Python 3.7; includes Windows API set (stub) DLLs and the Microsoft C runtime library. |
La Figura 7 muestra la estructura de directorios del archivo descomprimido que contiene la distribución de Python, listando sólo los archivos maliciosos que se incluyen dentro.
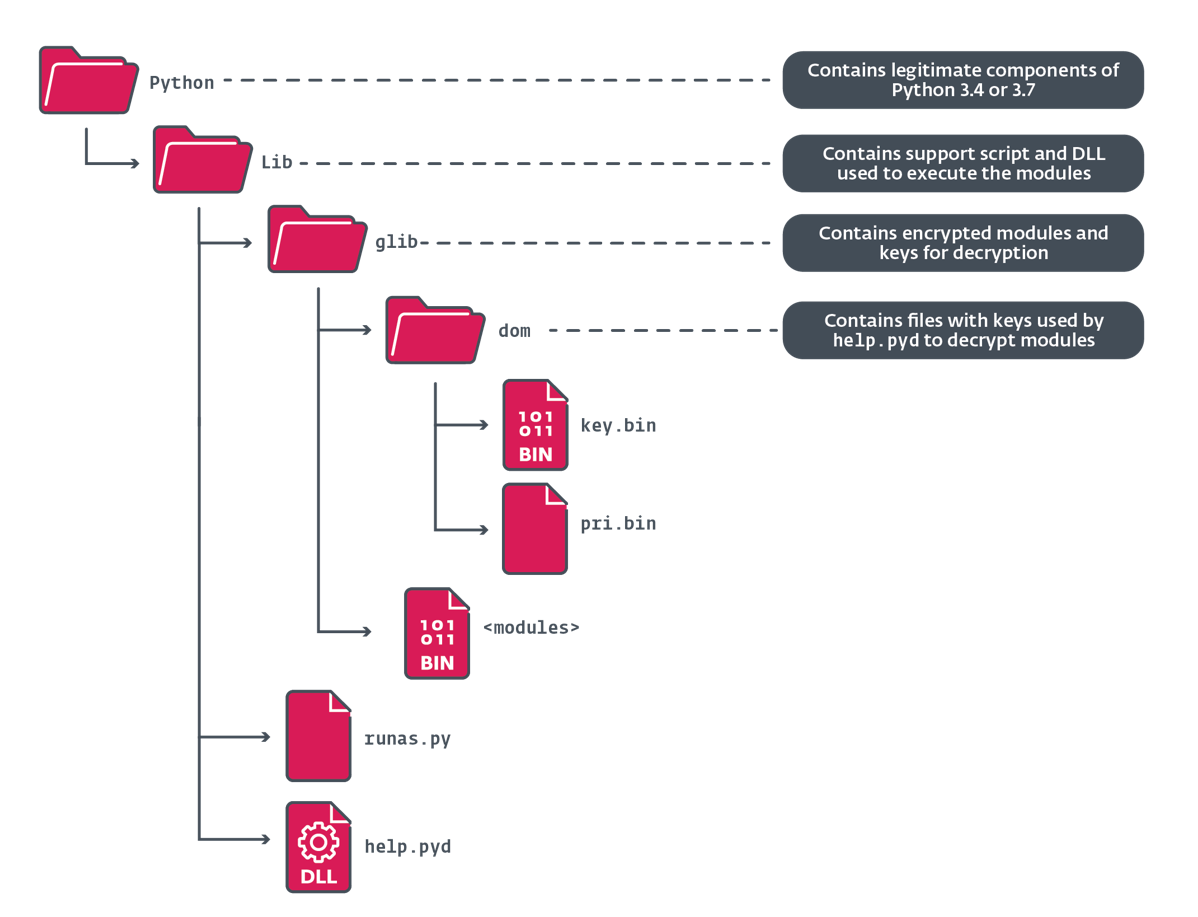
SlowStepper ejecuta el intérprete de Python utilizando la siguiente línea de comandos:
%PUBLIC%\Documents\WPSDocuments\WPSManager\Python\Pythonw.exe -m runas <nombre_modulo>
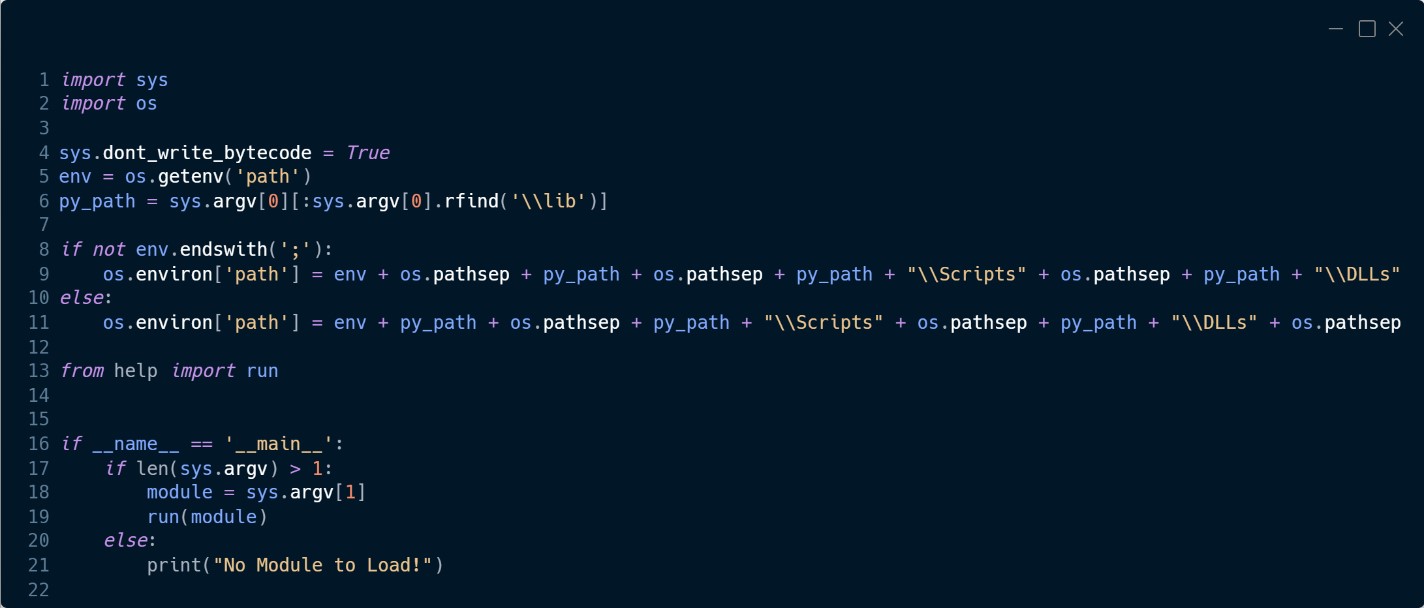
El módulo llamado runas es un script personalizado de Python (Figura 8) que carga otro módulo personalizado de Python llamado help desde el cual utiliza la función llamada run para desencriptar el módulo y ejecutarlo.
La Tabla 6 lista los módulos que recuperamos del repositorio remoto durante el tiempo que estuvo disponible.
Tabla 6. Lista de módulos Python y su propósito
| Filename on disk | Original module name | Purpose |
| 900150983cd24fb0 |
abc | Test module that prints hello world. |
| ef15fd2f45e6bb5c |
Browser | Collects a wide range of data from web browsers: Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge, Opera, Brave, Vivaldi, Cốc Cốc browser, UC Browser, 360 Browser, and Mozilla Firefox. |
| 967d35e40f3f95b1 |
Camera | If the computer has a camera connected, it takes photos. |
| a7ba857c30749bf4 |
CollectInfo | Scans the disk for files with extensions .txt, .doc, .docx, .xls, .xlsx, .ppt, and .pptx. Collects information from several software titles, including: LetsVPN, Tencent QQ, WeChat, Kingsoft WPS, e2eSoft VCam, KuGou, Oray Sunlogin, and ToDesk. |
| 6002396e8a3e3aa7 |
Decode | Downloads a module from the remote repository and decrypts it. |
| 9348a97af6e8a2f4 |
DingTalk | Collects a wide range of data from DingTalk (a corporate management tool developed in China), including chat messages, audio, video, contact information, and groups the user has joined. |
| 801ab24683a4a8c4 |
Download | Downloads (non-malicious) Python packages. |
| 16654b501ac48e46 |
FileScanner | Scans the disk for files, using the same code as CollectInfo. |
| 7d3b40764db47a45 |
FileScannerAllDisk | |
| 3582f6ebaf9b6129 |
getOperaCookie | Gets cookies from the Opera browser. |
| 10ae9fc7d453b0dd |
list | Lists modules with a .py extension. |
| ce5bf551379459c1 |
Location | Obtains the IP address of the computer and the GPS coordinates, using online services. |
| 68e36962b09c99d6 |
Location1 | |
| 5e0a529f8acc19b4 |
LocationByIP | |
| c84fcb037b480bd2 |
PackDir | Creates a ZIP archive of the specified file. |
| 4518dc0ae0ff517b |
qpass | This script appears to be unfinished. It obtains and decrypts passwords from Tencent QQ Browser. Probably replaced by the qqpass module. |
| 5fbf04644f45bb2b |
qqpass | Obtains and decrypts passwords from Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, Tencent QQ Browser, 360 Chrome, and UC Browser. |
| 874f5aaef6ec4af8 |
ScreenRecord | Records the screen, saving the result as an AVI file inside a ZIP archive. |
| c915683f3ec888b8 |
Telegram | Collects account information from the Telegram desktop application. |
| 104be797a980bcbd |
Webpass | Similar to the qqpass module. |
| e5b152ed6b4609e9 |
One of the largest modules, it collects a wide range of data from WeChat. | |
| 6d07a4ebf4dff8e5 |
Wechat_all_file | Collects data from WeChat. |
| 17cf4a6dd339a131 |
Wechat_src | |
| 8326cef49f458c94 |
Wechat1 | Similar to WeChat. |
| 427f01be70f46f02 |
WechatFile | |
| 72704d83b916fa1f |
WirelessKey | Collects wireless network information and passwords, and output from the ipconfig /all command. |
Además del conjunto de herramientas Python, encontramos almacenadas en el repositorio de código remoto otras herramientas (Tabla 7) que no están cifradas; algunas de ellas estaban programadas en C/C++ y otras en Go, como se indica a continuación.
Tabla 7. Herramientas y su función
| Tool filename | Description |
| agent.mod | Reverse proxy programmed in Go. |
|
getcode.mod getcode64.mod |
Mimikatz. This tool is a DLL downloaded by the getpwd command. |
| InitPython.mod | Old downloader to install the customized Python distribution on the compromised machine. This tool is a DLL. |
| Remote.mod | RealVNC server that allows the attackers to remotely control the compromised machine. This tool is a DLL. |
| soc.mod |
Reverse proxy programmed in Go. Signed with a certificate from a Chinese company called Hangzhou Fuyang Qisheng Information Technology Service Department. We were unable to find any information about the company. |
| stoll.mod |
Tool used to perform downloads, written in Go. Signed with a certificate from the Chinese company Zhoushan Xiaowen Software Development Studio. We were unable to find any information about the company. |
Conclusión
En este blogpost, hemos analizado un ataque a la cadena de suministro contra un proveedor coreano de VPN, dirigido a usuarios del este de Asia, como es evidente a través del software específico dirigido a la recopilación de información y confirmado a través de la telemetría de ESET. También documentamos el backdoor SlowStepper, utilizado exclusivamente por PlushDaemon. Este backdoor destaca por su protocolo C&C multietapa que utiliza DNS, y su capacidad para descargar y ejecutar docenas de módulos Python adicionales con capacidades de espionaje.
Los numerosos componentes del conjunto de herramientas PlushDaemon y su rico historial de versiones demuestran que, aunque desconocido hasta ahora, este grupo APT alineado con China ha estado operando diligentemente para desarrollar una amplia gama de herramientas, lo que lo convierte en una importante amenaza a tener en cuenta.
Para cualquier consulta sobre nuestra investigación publicada en WeLiveSecurity, por favor contáctenos en threatintel@eset.com.ESET Research ofrece informes privados de inteligencia APT y fuentes de datos. Para cualquier consulta sobre este servicio, visite la página de ESET Threat Intelligence.
IoCs
Puede encontrar una lista completa de indicadores de compromiso y muestras en nuestro repositorio de GitHub.
Archivos
| SHA-1 | Filename | Detection | Description |
| A8AE42884A8EDFA17E9D |
AutoMsg.dll | Win32/ShellcodeRunner.GZ | Initial loader DLL. |
| 2DB60F0ADEF14F4AB357 |
lregdll.dll | Win32/Agent.AGUU | Loader DLL for the SlowStepper backdoor. |
| 846C025F696DA1F6808B |
OldLJM.dll | Win32/Agent.AGXL | Installer DLL, internally named OldLJM.dll. It is extracted from EncMgr.pkg and executed in memory. |
| AD4F0428FC9290791D55 |
svcghost.exe | Win32/Agent.AGUU | Process monitor component that launches PerfWatson.exe or RuntimeSvc.exe to side-load lregdll.dll. |
| 401571851A7CF71783A4 |
main.dll | Win32/Agent.AEIJ | Decrypted SlowStepper backdoor component. |
| 068FD2D209C0BBB0C6FC |
IPanyVPNsetup |
Win32/ShellcodeRunner.GZ | Malicious IPany installer. Contains the SlowStepper implant and the legitimate IPany VPN software. |
Red
| IP | Domain | Hosting provider | First seen | Details |
| 202.189.8[.]72 | reverse.wcsset |
Shandong eshinton Network Technology Co., Ltd. | 2024‑10‑14 | Server used by the (reverse proxy) soc.mod tool. |
| 47.96.17[.]237 | agt.wcsset[.]com | Hangzhou Alibaba Advertising Co.,Ltd. | 2024‑10‑14 | Server used by agent.mod tool. |
| N/A | 7051.gsm.360safe |
N/A | 2020‑09‑29 | SlowStepper queries this domain to obtain its associated DNS TXT record. |
| 202.105.1[.]187 | st.360safe |
IRT-CHINANET-CN | 2021‑03‑11 | Fallback C&C server contacted by SlowStepper. |
| 47.74.159[.]166 | N/A | Alibaba (US) Technology Co., Ltd. | 2020‑09‑29 | SlowStepper C&C server. |
| 8.130.87[.]195 | N/A | Hangzhou Alibaba Advertising Co.,Ltd. | 2020‑09‑29 | SlowStepper C&C server. |
| 47.108.162[.]218 | N/A | Hangzhou Alibaba Advertising Co.,Ltd. | 2020‑09‑29 | SlowStepper C&C server. |
| 47.113.200[.]18 | N/A | Hangzhou Alibaba Advertising Co.,Ltd. | 2020‑09‑29 | SlowStepper C&C server. |
| 47.104.138[.]190 | N/A | Guowei Pan | 2020‑09‑29 | SlowStepper C&C server. |
| 120.24.193[.]58 | N/A | Hangzhou Alibaba Advertising Co.,Ltd. | 2020‑09‑29 | SlowStepper C&C server. |
| 202.189.8[.]87 | N/A | Shandong eshinton Network Technology Co., Ltd. | 2020‑09‑29 | SlowStepper C&C server. |
| 202.189.8[.]69 | N/A | Shandong eshinton Network Technology Co., Ltd. | 2020‑09‑29 | SlowStepper C&C server. |
| 202.189.8[.]193 | N/A | Shandong eshinton Network Technology Co., Ltd. | 2020‑09‑29 | SlowStepper C&C server. |
| 47.92.6[.]64 | N/A | Hangzhou Alibaba Advertising Co.,Ltd. | 2020‑09‑29 | SlowStepper C&C server. |
Técnicas ATT&CK de MITRE
Esta tabla se ha elaborado utilizando la versión 16 del marco MITRE ATT&CK.
| Tactic | ID | Name | Description |
| Resource Development | T1583.001 | Acquire Infrastructure: Domains | PlushDaemon has acquired domain names for its C&C infrastructure. |
| T1583.004 | Acquire Infrastructure: Server | PlushDaemon has acquired servers to be used as C&C servers. | |
| T1608.001 | Stage Capabilities: Upload Malware | PlushDaemon has staged its toolkit in the code repository website GitCode. | |
| T1608.002 | Stage Capabilities: Upload Tool | PlushDaemon has staged its toolkit in the code repository website GitCode. | |
| T1588.001 | Obtain Capabilities: Malware | PlushDaemon has access to SlowStepper. | |
| T1588.002 | Obtain Capabilities: Tool | PlushDaemon tools getcode.mod and getcode64.mod use Mimikatz. | |
| T1588.003 | Obtain Capabilities: Code Signing Certificates | PlushDaemon tools soc.mod and stoll.mod are signed. | |
| T1588.005 | Obtain Capabilities: Exploits | PlushDaemon has used an unidentified exploit for Apache HTTP server. | |
| Initial Access | T1659 | Content Injection | PlushDaemon can intercept network traffic to hijack update protocols and deliver its SlowStepper implant. |
| T1190 | Exploit Public-Facing Application | PlushDaemon exploited an unidentified vulnerability in Apache HTTP Server. | |
| T1195.002 | Supply Chain Compromise: Compromise Software Supply Chain | PlushDaemon has compromised the supply chain of a VPN developer and replaced the original installer with a trojanized one containing the SlowStepper implant. | |
| Execution | T1059.003 | Command-Line Interface: Windows Command Shell | SlowStepper uses cmd.exe to execute commands on a compromised machine. |
| T1059.006 | Command-Line Interface: Python | SlowStepper for Windows can use the Python console to execute the Python components of its toolkit. | |
| Persistence | T1547.001 | Boot or Logon Autostart Execution: Registry Run Keys / Startup Folder | The SlowStepper installer establishes persistence by adding an entry in HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\ |
| T1547.004 | Boot or Logon Autostart Execution: Winlogon Helper DLL | The SlowStepper process monitor component can establish persistence by adding an entry in HKLM\Software\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon\Userinit or HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon\load. | |
| T1574.002 | Hijack Execution Flow: DLL Side-Loading | PlushDaemon has abused a legitimate command line utility included in Visual Studio called regcap.exe to side-load a malicious DLL named lregdll.dll. | |
| Defense Evasion | T1222.001 | File Permissions Modification: Windows File and Directory Permissions Modification | SlowStepper modifies the access rights of the directory where its components are stored on disk. |
| T1070.004 | Indicator Removal: File Deletion | SlowStepper can remove its own files. | |
| T1036.005 | Masquerading: Match Legitimate Name or Location | SlowStepper uses folder names and filenames from legitimate software. | |
| T1112 | Modify Registry | SlowStepper can modify the registry. | |
| T1027.007 | Obfuscated Files or Information: Dynamic API Resolution | SlowStepper dynamically resolves Windows API functions. | |
| T1027.009 | Obfuscated Files or Information: Embedded Payloads | SlowStepper loader DLLs contain embedded, position-independent code, executed in memory, to load components. | |
| T1027.013 | Obfuscated Files or Information: Encrypted/Encoded File | SlowStepper components are stored encrypted on disk. | |
| T1553.002 | Subvert Trust Controls: Code Signing | PlushDaemon tools soc.mod and stoll.mod are signed. | |
| Discovery | T1217 | Browser Bookmark Discovery | SlowStepper’s Browser tool collects information from browsers. |
| T1083 | File and Directory Discovery | SlowStepper and its tools can search for files with specific extensions, or enumerate files in directories. | |
| T1120 | Peripheral Device Discovery | SlowStepper and its toolkit can discover devices connected to the compromised machine. | |
| T1057 | Process Discovery | SlowStepper can create a list of running processes. | |
| T1012 | Query Registry | SlowStepper can query the registry. | |
| T1518 | Software Discovery | SlowStepper can create a list of software installed on the compromised machine. | |
| T1082 | System Information Discovery | SlowStepper can collect system information. | |
| T1614 | System Location Discovery | SlowStepper’s Location tool attempts to discover the possible geolocation of the compromised machine by querying several online services. | |
| T1016 | System Network Configuration Discovery | SlowStepper collects information from the network adapters. | |
| T1016.002 | System Network Configuration Discovery: Wi-Fi Discovery | SlowStepper’s Wireless tool and its variants collects a wide range of information from the Wi-Fi network. | |
| T1033 | System Owner/User Discovery | SlowStepper obtains the username. | |
| Collection | T1560.002 | Archive Collected Data: Archive via Library | SlowStepper tools can compress the collected data in ZIP archives. |
| T1123 | Audio Capture | SlowStepper can capture audio if the compromised machine has a microphone. | |
| T1005 | Data from Local System | SlowStepper and its tools collect a wide range of data from the compromised system. | |
| T1074.001 | Data Staged: Local Data Staging | SlowStepper and its tools stage data locally before exfiltrating it to the C&C server. | |
| T1113 | Screen Capture | SlowStepper’s ScreenRecord tool can take screenshots. | |
| T1125 | Video Capture | SlowStepper’s Camera tool can record videos if the compromised machine has a camera. | |
| Command and Control | T1071.004 | Standard Application Layer Protocol: DNS | SlowStepper retrieves a DNS TXT record that contains an AES-encrypted list of C&C servers. |
| T1132.001 | Data Encoding: Standard Encoding | SlowStepper retrieves a DNS TXT record that contains an AES-encrypted list of C&C servers. The record is base64 encoded. | |
| T1573.001 | Encrypted Channel: Symmetric Cryptography | SlowStepper’s communication protocol with its C&C is encrypted with AES. | |
| T1008 | Fallback Channels | SlowStepper gets a fallback C&C server IP address by resolving an alternative domain controlled by the attackers. | |
| T1105 | Remote File Copy | SlowStepper downloads additional tools from a remote code repository at GitCode. | |
| T1104 | Multi-Stage Channels | SlowStepper obtains a list of C&C servers by querying the DNS TXT record from a domain controlled by the attackers; if no communication can be established with the servers, it resolves the IP address of another domain controlled by the attackers to obtain a backup server. SlowStepper tools use different servers from PlushDaemon infrastructure. |
|
| T1095 | Standard Non-Application Layer Protocol | SlowStepper communicates with its C&C via TCP. | |
| T1090 | Connection Proxy | SlowStepper tools agent.mod and soc.mod are reverse proxies. | |
| T1219 | Remote Access Tools | SlowStepper tool Remote.mod allows its operator to remotely control the compromised machine via VNC. | |
| Exfiltration | T1020 | Automated Exfiltration | SlowStepper can exfiltrate staged data. |
| T1041 | Exfiltration Over C2 Channel | SlowStepper exfiltrates collected data when connected to one of its C&C servers. |










